When you hear the word “conductor” your immediate thought might be a musical conductor.
However, there’s another type of conductor — an electrical material that works with an insulator to support items like your laptop computer, television, or smartphone.

Conductors and insulators work together but perform different roles. Each has an important function and purpose as they interact with power sources.
Knowing the difference between conductors and insulators will give you a better understanding of how energy transfers from one material to another in the world around you.
What's a Conductor?
Switch on a table lamp, turn on a gas stove, or plug in your laptop and you’ve used a conductor. It's material that transfers electrical power or thermal heat to your appliances, devices, and other items that need an energy source.
Key elements of a conductor:
A “metal” wire with high levels of conductivity that transfers energy
Electrical wires, which are connected to electronics and other appliances
Materials such as copper, silver, gold, nickel, iron, chromium, and steel that easily transmit electricity or thermal heat through them without resistance
Example of a conductor:
A gas cooker acts as a thermal heat conductor.
It transmits heat to a metal pan on a stovetop for the purpose of cooking the items in the pan.

What's an Insulator?
The insulator performs the opposite role of a conductor. It stops the flow of energy sources. An insulator insulates electrical energy and thermal heat to keep it from escaping — for example, a Styrofoam disposable cup keeps your coffee warm.

Key elements of an insulator:
A “non-metal” material with high levels of resistance that blocks the flow of energy
Covers wires that transmit electricity or heat to prevent electrocution and burns
Materials such as rubber, plastic, wood, glass, air, and paper
Example of an insulator:
A rubber-insulated thermos container is an insulator.
The rubber acts as an insulator to retain the heat of a hot beverage inside the thermos and prevent it from escaping.
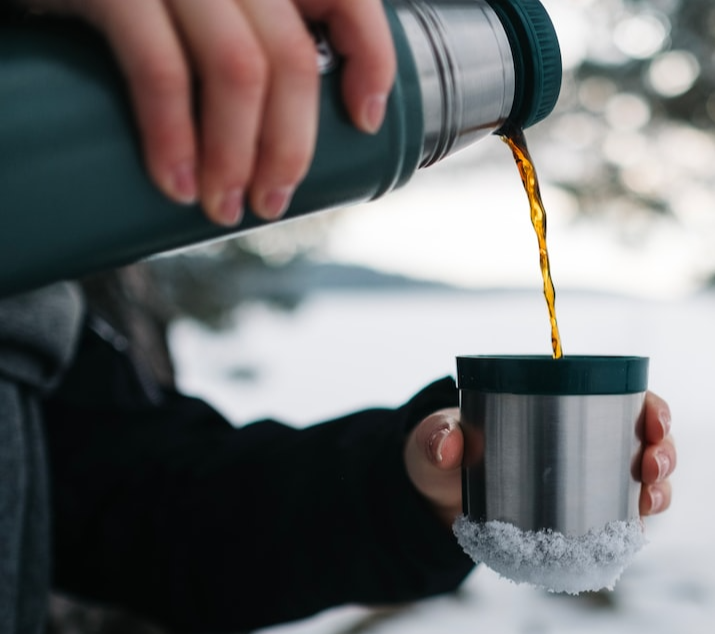

Is it a Conductor or an Insulator?
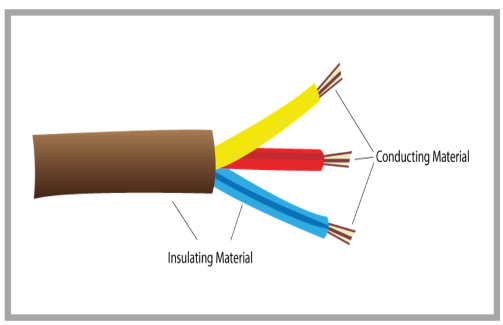
Here's an easy way to understand and remember the difference between conductors and insulators:
A conductor easily transfers energy that produces electricity and heat that quickly flows through it.
An insulator stops the transfer of energyand protects you from the dangers of electricity and heat when you touch it.
Different Uses and Applications
You can see multiple uses and applications of conductors and insulators in your home, school, office and other buildings, including outdoors.
Conductors
Power lines transmit electricity to homes, schools, hospitals, and businesses.
Plugs transfer power from wall sockets to connected electrical items.
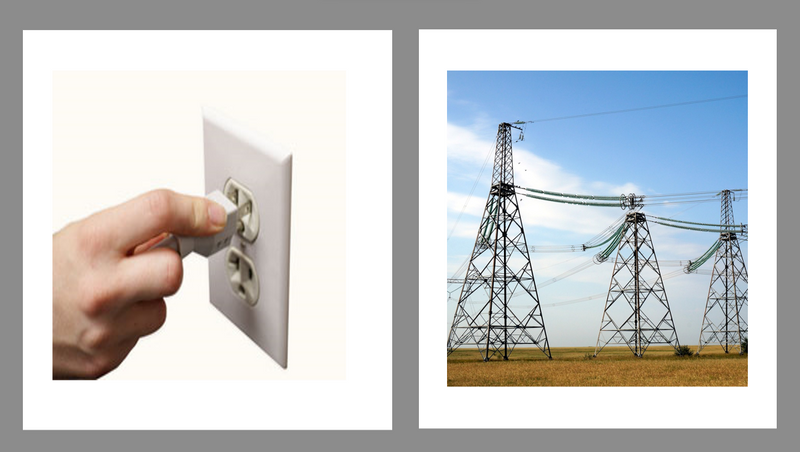


Insulators
Insulated cable extension cords isolate and protect electric conductor wires.
Styrofoam cups keep heat inside and the outside surface cool.
Plastic handles on a hot pan prevent the transfer of heat.
Knowledge Check ⚡
 Mollie is doing her homework, but finds it difficult to identify the difference between conductors and insulators from these examples:
Mollie is doing her homework, but finds it difficult to identify the difference between conductors and insulators from these examples:
A: Elijah eats lunch and looks at a field of huge towers of high voltage, electric power pylon lines.
B: Vance plugs the charger of his new smartphone and his desktop computer cable into a wall socket.
C: Dexter cooks Italian pasta and vegetables for supper in stainless-steel pans with metal handles on a gas stove.
D: Alexis exits her local coffee shop holding her favorite hot beverage in a Styrofoam cup and an onion bagel in a napkin.
Quiz
Which examples refer ONLY to conductors? Select all that apply:
Take Action

Learn more about the difference between conductors and insulators:
Your feedback matters to us.
This Byte helped me better understand the topic.
