Ever wonder why weather forecasts give a high and low temperature instead of just one number?
Image courtesy of storyset via Freepik
Imagine you're planning a trip and check the forecast. It says "high of 24 degrees Celsius." Perfect for sightseeing! But then you see another number, "low of 10 degrees Celsius." Brrrr! Maybe pack a jacket after all.
This is where variance comes in! Variance helps us understand how spread out the data points (temperatures in this case) are from the average (the high of 24 degrees Celsius).
Did you know?
Variance Explained
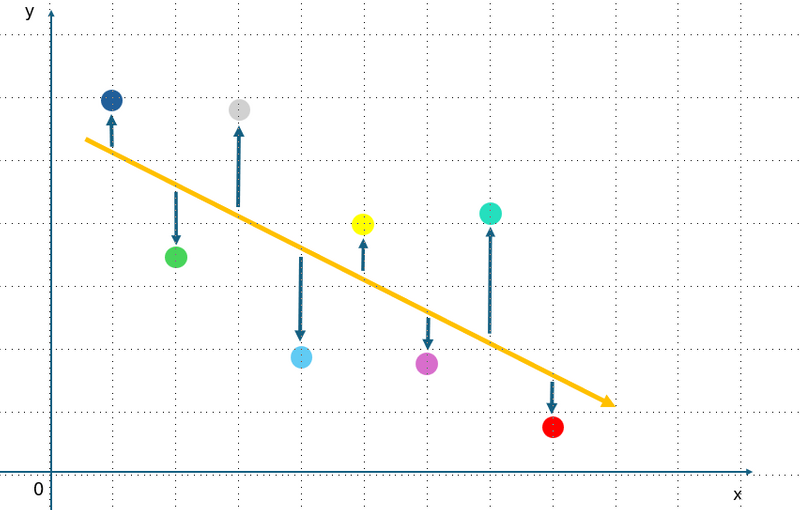 Image created by author using PowerPoint
Image created by author using PowerPoint
Variance is a measure of how much the values in a dataset differ from the mean (average) of the dataset — the set of numerical values for which you want to determine the spread.
Understanding variance is essential for statistical analysis and helps you understand data distribution.
To calculate the variance, you need to follow this formula:
Variance = Σ(xᵢ - μ)² / N
Where:
Σ represents the sum of the numbers in the dataset
xᵢ represents each individual value in the dataset
μ represents the mean of the dataset
N represents the total number of values in the dataset
In other words, the formula can be explained as:
Subtract the mean from each value in the dataset.
Square the result of each subtraction.
Sum all the squared differences.
Divide the sum by the total number of values in the dataset to calculate the variance.
Quiz
What does the symbol μ represent in statistical notation?
Did you know?
Step 1: Find the Mean (μ)
Dataset: [9, 14, 5, 8, 11, 7]
To workout the mean:
Add up all the values in the dataset.
Divide the sum by the total number of values to find the mean (μ).
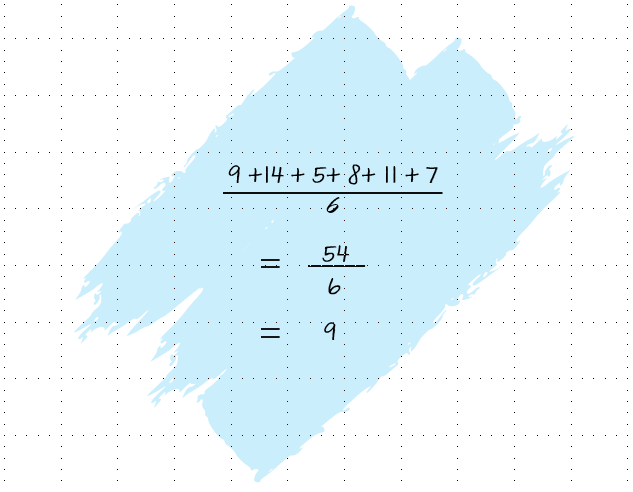 Image created by the author using PowerPoint. To hear an audio version of the information in the image above, click the play button on the audio player below:
Image created by the author using PowerPoint. To hear an audio version of the information in the image above, click the play button on the audio player below:
Quiz
What is the mean of the following dataset: 5, 8, 10, 12, 15.
Subscribe for more quick bites of learning delivered to your inbox.
Unsubscribe anytime. No spam. 🙂
Step 2: Calculate the Squared Differences (xᵢ - μ)²
For each value (xᵢ), subtract the mean (μ).
Square the result of each subtraction to get the squared differences.
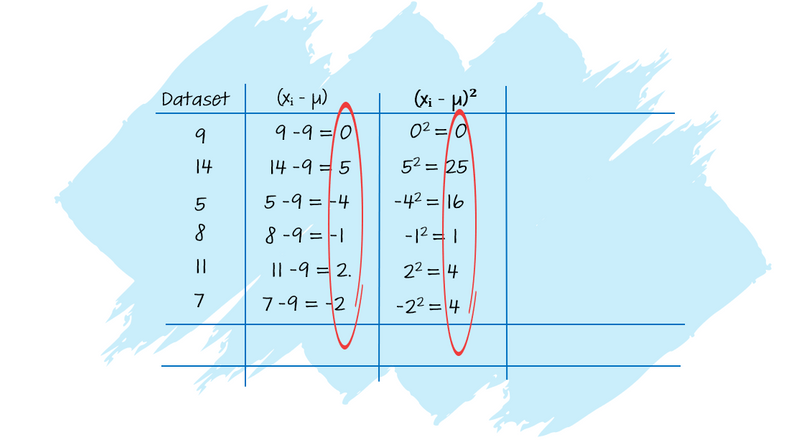
Image created by the author using PowerPoint. To hear an audio version of the information in the image above, click the play button on the audio player below:
Quiz
How many steps are there when working out the squared difference?
Step 3: Sum all the Squared Differences
Sum all the squared differences obtained in the previous step.
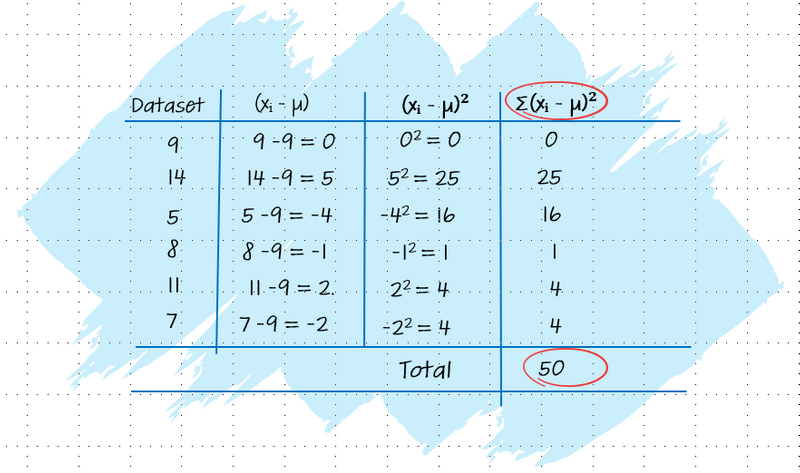 Image created by the author using PowerPoint. To hear an audio version of the information in the image above, click the play button on the audio player below:
Image created by the author using PowerPoint. To hear an audio version of the information in the image above, click the play button on the audio player below:
Quiz
The ages (in years) of 4 plants in a greenhouse are: 2, 3, 5, and 7. What is the sum of their squared difference?
Did you know?
Step 4: Compute the Variance
Divide the sum of squared differences by the total number of values in the dataset to get the variance.
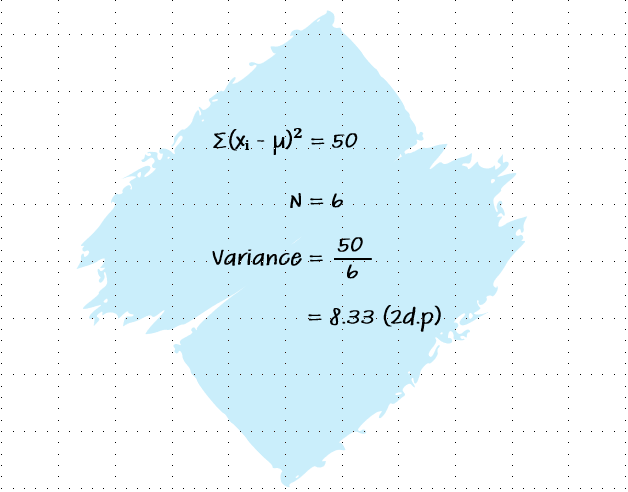 Image created by the author using PowerPoint. To hear an audio version of the information in the image above, click the play button on the audio player below:
Image created by the author using PowerPoint. To hear an audio version of the information in the image above, click the play button on the audio player below:
Quiz
Here are the ages of 5 employees. What is their age variance? 30, 45, 20, 50, 35. (Population Variance (σ²): σ² = Σ (xᵢ- µ) ² / N)
Did you know?
Take Action

Now that you're able to calculate variance, you can take your data analysis a step further by completing the tasks below:
Your feedback matters to us.
This Byte helped me better understand the topic.
