Almost 2 million Americans are currently incarcerated. Many of these prisoners (about 75%) must hold a prison job or be subjected to further punishments (e.g., loss of visitation rights).
 Image courtesy of Wikimedia Commons
Image courtesy of Wikimedia Commons
But who benefits most from prison labor?
Prison labor is a controversial topic that some view as "forced labor" and an infringement of the 13th Amendment of the US Constitution:
Neither slavery nor involuntary servitude, except as a punishment for crime whereof the party shall have been duly convicted, shall exist within the United States.
Did you know?
The Economics of Prison Labor
Prisoners must be housed, fed, and clothed. The median cost per prisoner (as of 2021) was $64,865, though Massachusetts spent over $300,000 per prisoner. These costs are paid by state and federal governments.
 Infographic courtesy of American Civil Liberties Union. To hear an audio description of the text in the infographic, press play on the audio player below.
Infographic courtesy of American Civil Liberties Union. To hear an audio description of the text in the infographic, press play on the audio player below.
Who Benefits?
Companies take advantage of competition for local low-wage jobs:
Companies can pay 52 cents per hour to the prisoner vs. $7.25 per hour (minimum wage in 34 states) to a non-incarcerated worker.
It costs about $80 million per year to feed, house, and clothe prisoners but this money is made up for by the $374 million in revenue generated by the work prisoners do for private companies.
Meanwhile, after leaving prison and re-entering society, fewer than 20% of former prisoners find work that pays more than $15,000 annually. Nearly two-thirds of former prisoners remain unemployed a year after their release.
Did you know?
The Prisoner's Workday
 Image courtesy of Wikimedia Commons
Image courtesy of Wikimedia Commons
At one typical medium-security prison:
Prisoners do landscape work, for which they are paid $1.76 for 8 hours of labor.
At this same location, prisoners also work as a tutor, library aid, or food service worker for a salary of up to $2.66 per day.
The median salary (2022) for landscapers who aren't in prison was $35,890 per year.
The landscaper incarcerated in the medium-security prison listed above can expect to earn about $431 per year.
Tutors earn an average of $20 per hour and typically don't tutor full time. If they tutor 20 hours per week, their annual salary is around $26,000.
The prisoners who work as a tutor can expect to earn about $691 per year. This is based on an 8 hour day.
Rehabilitation or Exploitation?
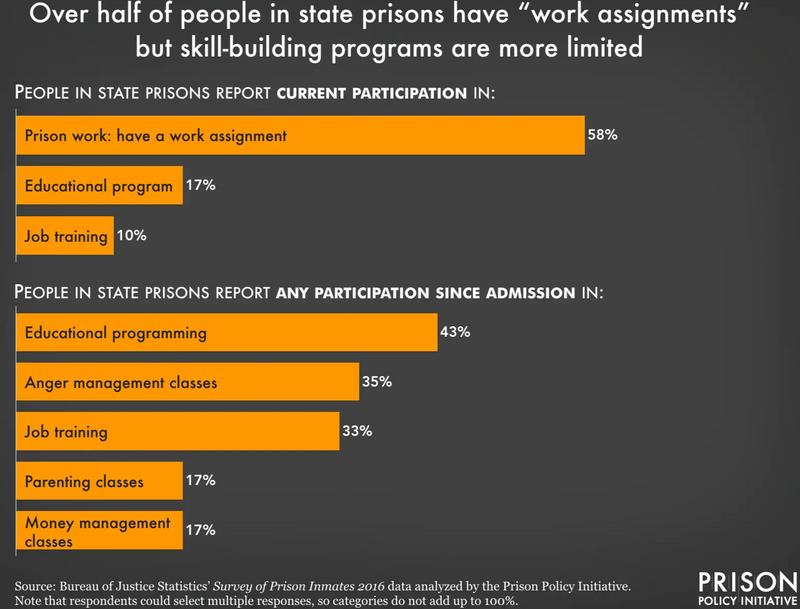
Infographic courtesy of the Prison Policy Initiative. To hear an audio description of the text in the infographic, press play on the audio player below.
Prison labor may have some benefits for prisoners:
Some prisoners do gain skills during their incarceration such as cooking and manufacturing.
Prisoners who didn't complete high school before prison can earn their GED in prison.
Anger management classes help prisoners to manage their emotions and redirect negativity into positive channels.
The RAND Corporation (a non-profit think tank) has found that prisoners who get an education while incarcerated are 43% less likely to return to prison after their release.
Did you know?
Subscribe for more quick bites of learning delivered to your inbox.
Unsubscribe anytime. No spam. 🙂
Take Action
 Photo by Bermix Studio on Unsplash
Photo by Bermix Studio on UnsplashTake the time to learn more about the effects of prison labor:
Your feedback matters to us.
This Byte helped me better understand the topic.
