This logo isn't an ad or affiliate link. It's an organization that shares in our mission, and empowered the authors to share their insights in Byte form.
Rumie vets Bytes for compliance with our
Standards.
The organization is responsible for the completeness and reliability of the content.
Learn more
about how Rumie works with partners.
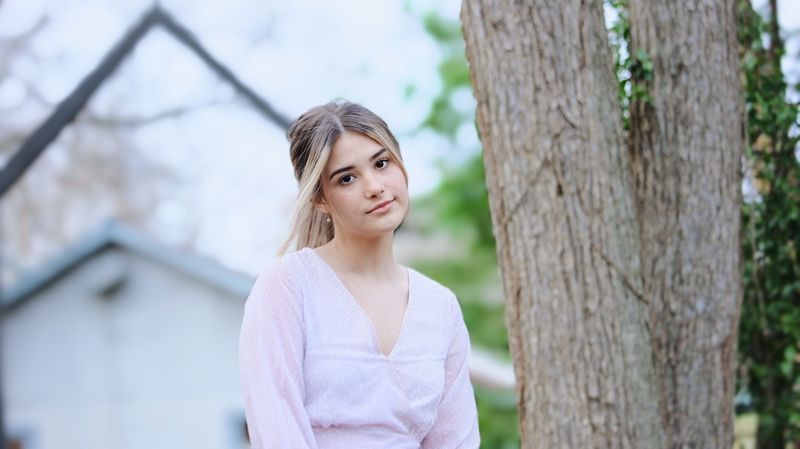
Have you ever tried to blend in to avoid being seen or having to talk to someone?

At some point, we've all avoided an uncomfortable person, place, or situation. If you find that you're constantly avoiding certain things in your life, you may have avoidance anxiety.
What Is Avoidance?
 Photo by Priscilla Du Preez on Unsplash
Photo by Priscilla Du Preez on UnsplashAvoidance is a way to cope with feelings, thoughts, or situations that may be difficult and is often a sign of anxiety.

Things teens may avoid as a result of avoidance anxiety:
social situations
extracurricular activities
school
certain foods
family members
dating
work
travel
Avoidance is appropriate when... 👍
there is a dangerous situation.
you're experiencing peer pressure.
Avoidance is concerning when... 🚩
it impacts your academic, career, or personal growth.
it costs you time in your daily life.
1. Situational Avoidance
In teens, situational avoidance could look like:
Driving a longer route to avoid having to drive over a bridge. 🌉
Quitting the basketball team to avoid having to be around an ex-friend. 🏀
Cleaning the house to avoid working on the big assignment that is due the next day. 🧹
2. Cognitive Avoidance

In teens, cognitive avoidance could look like:
chronic worrying and/or obsessive thoughts.
constantly thinking about the "what ifs?"
rituals intended to avoid or drown out thoughts or feelings.
3. Protective Avoidance

This type of avoidance is often called obsessive compulsive disorder or OCD. A person with OCD performs time-consuming rituals in an effort to create a feeling of safety and avoid feelings of anxiety.

In teens, protective avoidance could look like:
compulsively cleaning
counting objects, time, steps, etc
using good luck charms
checking locks or doors
perfectionism
only eating certain foods
4. Somatic Avoidance

 Many situations that a person avoids could be a positive experience, but because they produced a physical response in the person, they're often avoided.
Many situations that a person avoids could be a positive experience, but because they produced a physical response in the person, they're often avoided.
In teens, somatic avoidance could include avoiding:
falling in love ❤️
speaking in front of people 🗣
being in new situations 🏫
intense workouts 💪
exciting events 💐
driving a car 🚙
5. Substitution Avoidance

 Internal
Internal
replacing one feeling with another that is easier to deal with at the time
the replacement could be grief instead of anger
 External
External
replacing a feeling with something that allows the person to cope with emotional pain
the replacement could be drugs, alcohol, gambling, food, risky behaviors, sex, internet gaming, etc.
Meet Junie
Junie is a junior in high school who has always been social. Recently, Junie's mom noticed that she hasn't been going out with her friends. Instead, Junie stays in her room and cleans.
When Junie's mom asked her why she isn't going out with friends, Junie shared that she "just likes to have a clean room" so she can find things, be organized for school, and sleep well.
Junie's mom wondered if there was more to the situation so she continued asking questions. She learned that Junie had also recently had an argument with her friend group. They're upset with Junie for "ditching" them all the time, even though she is just staying home. They don't believe her and Junie just doesn't want to deal with it.
Quiz
What type(s) of avoidance might Junie be displaying?
Junie might be displaying several types of avoidance. It sounds like, from what we have learned from Junie's mom, she's avoiding dealing with her friends because she doesn't want to deal with the fact that they're upset with her. Instead of having a confrontation with them, she is just avoiding them altogether. This would be an example of situational avoidance. She may also be showing signs of protective avoidance by compulsively cleaning her room in order to manage her feelings and to feel in control of her environment. As you can see, there can be overlap between different types of avoidance.
Take Action

Do you think you might have avoidance anxiety?
This Byte has been authored by
Sandi McKinney
Instructional Designer/eLearning Developer

 It involves:
It involves:
