
This logo isn't an ad or affiliate link. It's an organization that shares in our mission, and empowered the authors to share their insights in Byte form.
Rumie vets Bytes for compliance with our
Standards.
The organization is responsible for the completeness and reliability of the content.
Learn more
about how Rumie works with partners.

You're an excited student teacher ready to make your mark on the world! You buzz in to meet your seasoned teacher mentor who has much wisdom to pass on to the next generation of teachers.
She asks to review your lesson plans. You nervously hand her your lessons, and she quickly realizes that you need a crash course in direct instruction lesson planning.

With a reassuring smile, she invites you to her desk and begins to teach you the 6 steps to writing a direct instruction lesson.
What is Direct Instruction?
 Photo by National Cancer Institute on Unsplash
Photo by National Cancer Institute on UnsplashDirect instruction is the most traditional teaching method. It uses lectures to teach students. This method of teaching relies on one-way communication, with the teacher as the speaker and students listening while taking notes.
Check out the video below for more information about direct instruction. 🔽
1. Lesson Objective

A learning objective is a statement that says what learners will be able to do at the end of a lesson. In direct instruction, all lessons must have a learning objective.
It's important that objectives are both specific and measurable. This means the objective clearly states the goal and how success is measured.
One way to ensure this is to use Bloom's Taxonomy.Bloom's taxonomy is a teaching framework that categorizes learning goals, skills, and activities.
This allows teachers to assess if learners have met learning goals.
Check out these lesson objectives below.

Students will label the solar system with 80% accuracy.
Students will label the solar system [specific: the action students will perform]
with 80% accuracy [measureable: how we measure how successful learners are].
Students will correctly solve 30 multiplication facts within 3 minutes.
Students will correctly solve 30 multiplication facts [specific: the action students will perform]
within 3 minutes [measurable: how we measure how successful learners are].
Quiz
Which part of the objective is missing: "Students will match pictures of food to the correct food group. "
This objective is specific. It tells what students will do. However, it doesn't say how success is measured. To make this objective complete, add the following: "Students will match pictures of food to the correct food group with 90% accuracy."
2. Lesson Opener
A lesson opener gets learners ready for instruction. This is critical, as it sets the stage for the rest of the lesson.
During this step, the teacher should capture the audience’s attention and determine what students already know about a subject.
There are numerous ways to open a lesson. A teacher may consider asking a question or showing a short video clip. For more ideas for lesson openers, take a look at 10 Engaging Lesson Hooks.
3. Teacher Instruction
The teacher presents the lesson's objective and new information to learners.
The most frequent strategy used in this stage is modeling. Modeling happens when the teacher shows step-by-step instructions on how to complete the lesson's goal.
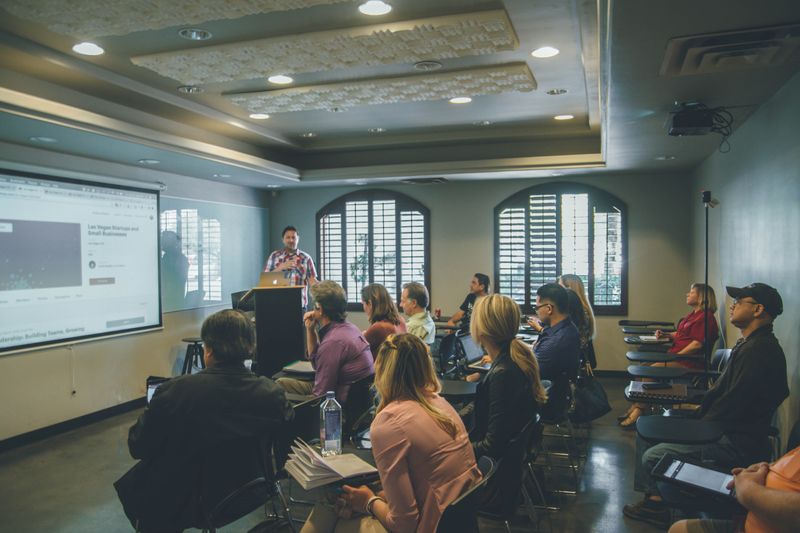 Photo by Kenny Eliason on Unsplash
Photo by Kenny Eliason on UnsplashThe teacher should use many examples and illustrations while modeling. This ensures that learners have numerous opportunities to understand particular concepts and skills and retain new knowledge.
Quiz
Which direct instruction strategy would help a teacher explain how to write a 5 paragraph essay to students?
To teach this skill, the teacher should model how to write an essay. In later lessons, a teacher may opt to give example essays or ask students to write an essay, but that will come after direct instruction.
Guided and Independent Practice

After teacher instruction, students practice the skill they were just taught.
There are two forms of practice. Guided practice should be completed before independent practice.
4. Guided Practice
Students practice the skill with the assistance of the teacher or other students. The teacher may put students into small groups for them to work together to complete a practice task.
During this time, the teacher should provide feedback and correct any mistakes.
5. Independent Practice
Following guided practice, students then independently practice the lessons' skills on their own. This again provides another opportunity for students to practice their newfound knowledge.
The goal for the new knowledge is to become automatic with practice.
Quiz
A teacher has modeled how to write a 5 paragraph essay to their class. Which activity can be used for independent practice?
Independent practice happens when students practice the skill their teacher modeled without any assistance. The teacher modeled writing a 5 paragraph essay, so the best independent practice activity is for them to write their own essay.
Did you know?
Independent practice can double as an assessment for teachers to see how well students performed with the new skills. Teachers can use this to reteach any missed points.
6. Review and Closure
During this stage, the teacher reviews the main ideas of the entire lesson,addresses any mistakes,and answers any lingering questions.
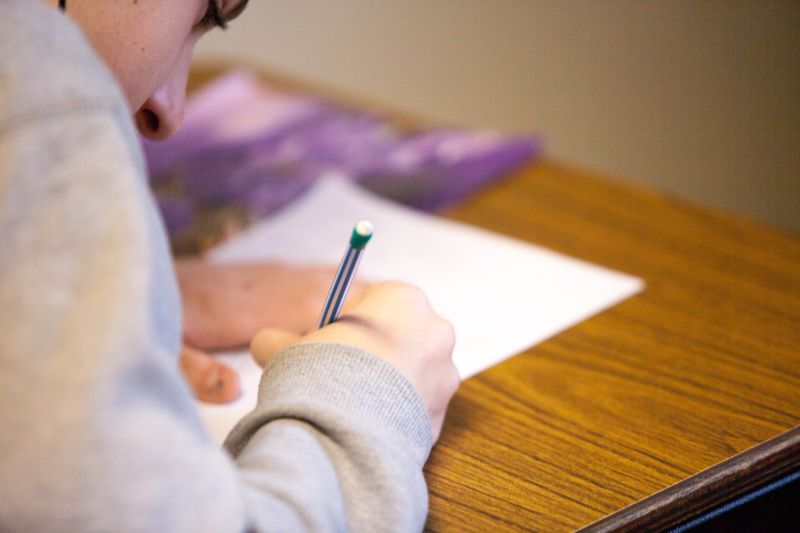 Photo by Ben Mullins on Unsplash
Photo by Ben Mullins on UnsplashAnother popular practice during this step is formative assessments.
A formative assessment is a test that measures how much content/skill a learner has mastered, for example, by using knowledge checks or exit tickets.

Knowledge Checks
This is usually a 1-2 question quiz given during a lesson to see if learners understand what was just taught.
A teacher may reteach, remodel, or continue with the lesson based on the data from the knowledge check.
Example
After modeling how to solve a multiplication equation using the traditional method, students will:
Use the traditional method to solve the following equation 6 x 7.
Use the traditional method to solve the following equation 4 x 5.

Exit Tickets
These are usually 1-5 questions quizzes given at the end of a lesson. Exit tickets pose questions about the whole lesson rather than just a lesson part like a knowledge check.
The teacher can then reteach missed points to students the next day, providing further feedback to students before a final test.
Example
At the end of the lesson on how to solve a multiplication equation using the traditional method, students will:
Rate from 1-3 (3 being very confident) how confident they are using the traditional method to solve multiplication equations.
Use the traditional method to solve 5 x 7.
Use the traditional method to solve 12 x 12.
Go over any questions or concerns they still have about using the traditional method to solve multiplication equations.
Take Action

Would you like some more practice with writing direct instruction lesson plans? Check out these tips:
This Byte has been authored by
Alicia Hedrington
Instructional Designer