This logo isn't an ad or affiliate link. It's an organization that shares in our mission, and empowered the authors to share their insights in Byte form.
Rumie vets Bytes for compliance with our
Standards.
The organization is responsible for the completeness and reliability of the content.
Learn more
about how Rumie works with partners.
Have you ever got to a point in life where you had to choose between your wants and needs?

It's key that you understand the difference between a want and a need. This will help you make decisions that lead to long-term well-being and personal fulfillment.
Maslow's hierarchy of needs will give you a way to prioritize your most basic needs before pursuing your desires.
What's the Difference between a Want and a Need?

Needs
These are the basicrequirements for survival and well-being.
Needs are universal and must be met for a person to live a stable, healthy life.
Examples: food, water, shelter, clothing, safety, emotional support.
Why needs are important: Failure to meet needs might result in physical or psychological harm.

Wants
These are things we desire (want) but aren't necessary for survival.
Wants are subjective and different from person to person.
Examples: designer clothes, latest gadgets, luxury vacations, dining out.
Why wants are important: Wants can improve our lives but should only be pursued when our needs have been met.
Did you know?
In some situations, what starts as a want can become a need!
For example, a smartphone might be considered a want, but for someone whose job depends on constant communication, it becomes a need. 📱
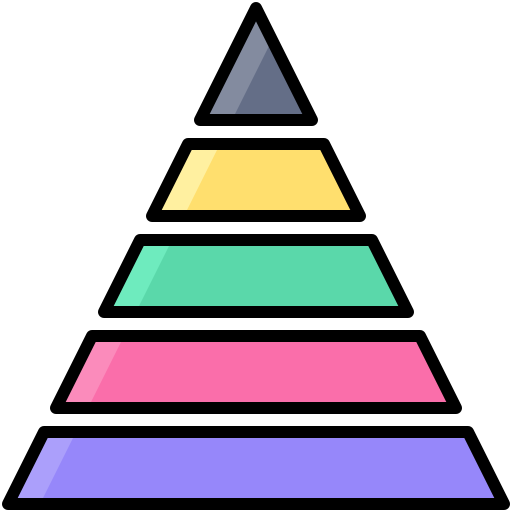
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
Maslow's hierarchy is a psychological theory that divides human needs into five levels, arranged in a pyramid.
According to this theory, people must satisfy lower-level needs before they can focus on higher-level desires. The base of the pyramid represents basic needs. As you move up the pyramid, you get closer to fulfilling desires.
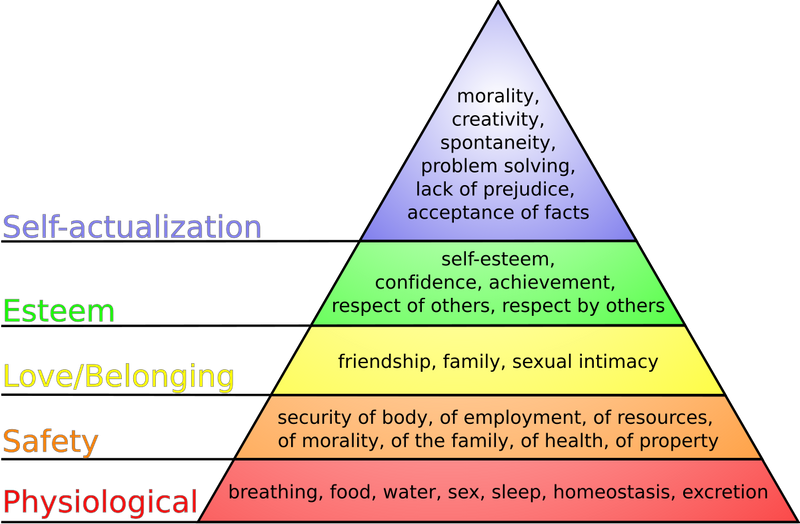 Image courtesy of J. Finkelstein, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons. To hear an audio description of the image, select play on the audio player below:
Image courtesy of J. Finkelstein, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons. To hear an audio description of the image, select play on the audio player below:
1. Physiological Needs
Basic needs required for survival.
Examples: food, water, warmth, and rest.
Key insight: If these needs aren't met, it's impossible to concentrate on anything else.

2. Safety Needs
This includes personal and financial security, health and well-being, and protection from accidents, illnesses, and emotional harm.
Examples: walking safely at night, having a stable job, being in good health.
Key insight: Once physiological demands are addressed, safety takes priority. A sense of security enables you to have a sense of control and make plans for the future.
3. The Need for Love and Belonging
Emotional needs that humans have for interpersonal relationships, affiliation, togetherness, and group membership.
Examples: a close group of friends, a romantic partner, being close with parents and siblings.
Key insight: Humans are social beings. Feeling liked and accepted is essential for our mental health.
 4. Esteem Needs
4. Esteem Needs
The need for respect, self-esteem, and recognition.
Examples: earning a promotion at work, winning an award, building a reputation as an expert in a field.
Key insight: After securing basic needs and social connections, people seek respect from others and themselves.
 5. Self-Actualization
5. Self-Actualization
Achieving full potential and pursuing personal growth.
Examples: pursuing a passion/creative project, mentoring others to share knowledge and skills, volunteering to make a meaningful impact, learning a new language or skill for self-improvement
Key insight: This is the highest level of Maslow's hierarchy, where someone strives to be the best versions of themselves.
Quiz
According to Maslow's hierarchy of needs, which level should you satisfy first before you can strive for self-actualization?
Physiological needs include the most basic requirements such as food, water, and rest. According to Maslow's hierarchy, these must be addressed before a person can focus on higher goals such as feeling protected, being loved, or realizing their desires. Without these basic necessities, it is difficult to think about anything else.
Applying Maslow’s Hierarchy to Decision-Making
When making decisions, especially those involving resources like time, money, or energy, figure out if you're meeting a need or a desire.

#1 Assess your current needs
Identify which level of Maslow's hierarchy you're currently focused on. Are your basic needs met, or are you still working on fulfilling them?
#2 Prioritize needs over wants
Before spending money or effort on a want, make sure your necessities are met.
For example, if you're considering purchasing a luxury item, make sure you have enough money for emergencies (a safety need).

#3 Use hierarchy as a decision-making tool
Ask yourself these kinds of questions before making a decision:
Does this decision help me fulfill a basic need?
How will this decision affect my safety, relationships, and self-esteem?
Will this decision allow me to grow and achieve my greatest potential?

#4 Long-term vs Short-term satisfaction
Needs typically provide long-term happiness, whereas wants may only provide short-term pleasure.
Consider the long-term consequences of your decisions.
Did you know?
Marketers often design ads to tap into your wants rather than your needs, encouraging impulsive decisions. Being aware of this can help you apply Maslow's hierarchy more effectively to resist unnecessary purchases.
For example, skincare brands frequently suggest that you need a particular product to achieve healthy skin.
Using the Hierarchy in Everyday Decisions
Consider the following scenarios regarding everyday life.

Scenario 1: You’re considering quitting your job to start a business.
Analysis: Check if your safety needs (financial stability, health insurance) are met before making the leap. If they are, and you have strong support networks (love and belongingness), then pursuing this want could lead to self-actualization.
Scenario 2: You’re thinking about buying an expensive gadget.
Analysis: Ensure your physiological and safety needs aren't compromised by this purchase. If those needs are secure, and the gadget will make you more productive or give you a better quality of life, it could be worth it. Otherwise, it may just be a want.
Scenario 3: You feel stressed and disconnected from loved ones due to work.
Analysis: Reevaluate your priorities. If work is affecting your need for love and belonging, consider steps to restore balance, like setting boundaries or spending more quality time with family and friends.
Quiz: Alex's Dilemma

Alex is a college student who just received a small inheritance from a relative. He is considering using the money to buy a new gaming console, something he has wanted for a long time. However, he also has student loans to pay off and no emergency savings.
Quiz
Using Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, what should Alex consider before deciding how to spend his inheritance?
Alex should focus on fulfilling his basic financial needs, which fall under the category of safety needs. While the gaming console might offer short-term enjoyment or social benefits, ensuring financial stability by paying off loans and having emergency savings is more important for his long-term well-being.
Take Action
Understanding the difference between a want and a need is important. Using Maslow's hierarchy of needs in your decision-making can help you live a more balanced and satisfying life.
Focusing on your basic needs first builds a solid foundation. This helps you to pursue your ambitions with confidence and clarity.

This Byte has been authored by
Divya Sharma
Instructional Designer
E-learning Design, B.Ed
