
A webpage contains information delivered in different forms like:
text
images
audio
video
A webpage is provided by a website and can be accessed through your computer browser using the web page URL.
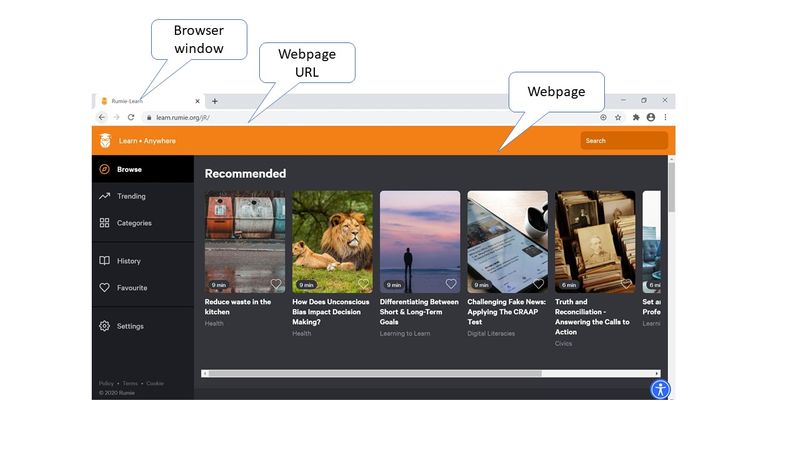
Learn how webpages work by watching the video below.
Basic Parts of a Webpage
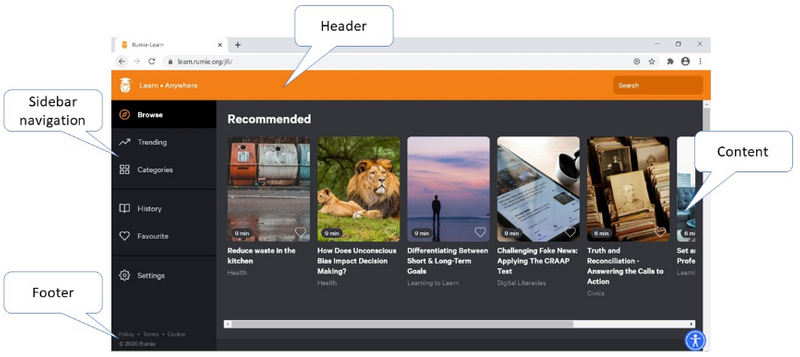
Header or Banner: Located at the top of a webpage. It can include the company logo, a title and sometimes a search box for the site. The header usually stays consistent for all webpages on a website.
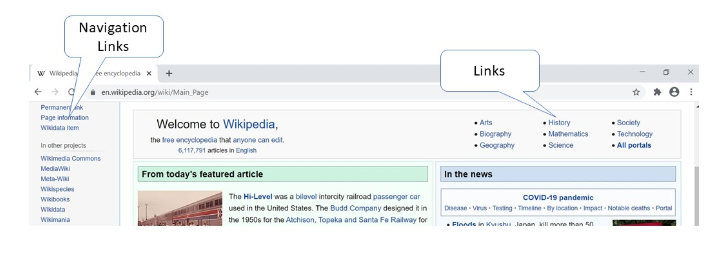
Navigation Bar: These are usually placed below the Header/Banner bar. The Navigation Bar lets you check out other pages on the website quickly and easily, as it is available to you no matter which page you are accessing.
Sidebar: Provides additional content, navigation or display ads. Not all webpages have sidebars.
Content: The main part of a website will be dedicated to content, as this is the main value of the site. Website content can contain text, video, images, or any combination of the three!
Footer: Located at the bottom of the page and usually provides links to contact information, company address, company information, terms of service, and social media links.
Quiz
Where would you normally find the contact information on a website?
Additional Webpage Elements
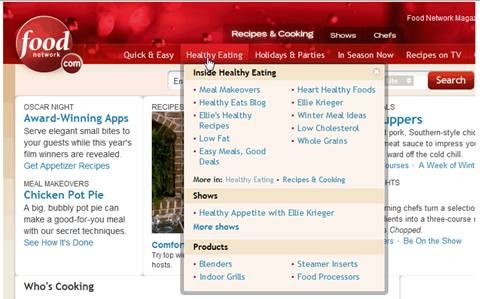
Menu: Provides a way to easily navigate a website. It's located in an easy-to-find place. A menu is often contained in the header, or on a collapsible pane (especially in mobile views of websites), and allows navigation through the pages of the website.
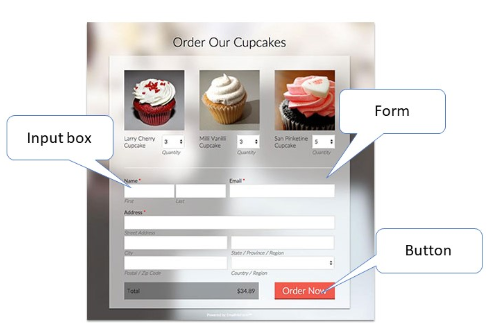
Forms: An easy way to capture information from website visitors. Contact and sign-up forms are very common.
Input Boxes: Captures specific pieces of information like a user name, an email address, a booking date for travel reservation, etc. and are often found in forms.
Buttons: Used to confirm a user's action, like the navigation to another webpage or submission of the information on a form.
Links: Used to navigate to a section of a webpage or to other webpages. Links can be included in any part or the webpage, especially in navigation bars and menus. You can often identify a link as a part of the text that is underlined or in a different colour.
Tips for Reading a Webpage
Take Action
Visit a webpage on a topic you're interested in!
In your browser type: www.google.com
In the search box enter a term you're interested in (e.g. dogs, computing, etc.)
Select a webpage from the results
Show a friend the webpage and explain the different parts to them!
Your feedback matters to us.
This Byte helped me better understand the topic.
