Have you ever wanted to send secret messages or communicate in code when words just wouldn't do?

Imagine you're in a situation where you need to share information without speaking or texting — perhaps in an emergency, or even just for fun with friends. Morse code can be your secret weapon! Let’s dive into the world of dots and dashes to unlock the art of silent communication.
History of Morse Code
The idea of sending electric signals through wires goes back as far as the early 1700s, and by 1798, a simple version of the telegraph was already being used in France.
In 1832, Samuel Morse, a professor at New York University, began working on his own version of the telegraph. Just a few years later, in 1835, he introduced Morse code — a system that translates letters into sounds using unique patterns.

Morse code is a way to send messages using sound or visual signals, with each letter of the ABC alphabet represented by a specific combination of short and long signals, often referred to as dots and dashes, or “dits and dahs".
Here is an example of words written in Morse Code:
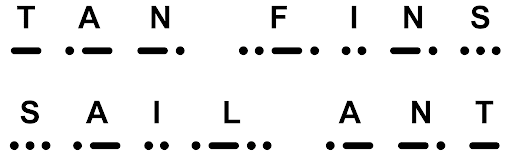 Image courtesy of NatRadioCo
Image courtesy of NatRadioCo
The first telegraph message was sent in 1844 from Washington, D.C., to Baltimore, and by 1866, a line connected the U.S. to Europe. Though later replaced by the telephone and the Internet, the telegraph greatly impacted communication.
 Photo by Amsterdam City Archives on Unsplash
Photo by Amsterdam City Archives on UnsplashMaster the Alphabet
Here’s your key to unlocking Morse code: the complete alphabet of dots and dashes. Use this guide to start translating letters into code and back again.
 Listen to Morse code to hear how each letter of the alphabet sounds.
Listen to Morse code to hear how each letter of the alphabet sounds.
 Look at the entire Morse code alphabet below and learn the dots and dashes for each letter of the alphabet.
Look at the entire Morse code alphabet below and learn the dots and dashes for each letter of the alphabet.
 To hear an audio version of the alphabet above, click play on the audio player below:
To hear an audio version of the alphabet above, click play on the audio player below:
Use this resource to learn Morse code quickly: Fastest Way to Learn Morse Code
Practice Listening and Transcribing
To successfully master Morse code, you need to spend time practicing, listening to, and transcribing it.
Here are some practical tips for improving your listening and transcribing skills in Morse code:
Start slow: Begin with slower speeds and gradually increase the pace as you become more comfortable with the sounds.
Focus on rhythm: Pay attention to the unique rhythm of dots (short sounds) and dashes (long sounds) to help distinguish between different letters and symbols.
Practice with short bursts: Work on transcribing small groups of letters or numbers before moving on to full words and sentences.
Repeat and replay: Listen to the same sequences multiple times to reinforce your recognition of each symbol.
Use a reference sheet: Keep a Morse code chart nearby to check your transcriptions and build familiarity with the patterns.
Practice daily: Short, consistent practice sessions will help you gradually improve both accuracy and speed.

Use this resource for translating Morse code: Morse Code Generator
Practice and test your listening skills:Morse Code Audio Practice Test
Here is a great free online course for learning the Morse code: Morse Code Ninja
Quiz
You're in an emergency situation. Which of the following emergency signals would you choose to get help?
Is Morse Code Still Used Today?
The short answer is yes. Organizations such as the Long Island CW Club conduct classes on teaching Morse code and provide opportunities to connect with other members.
 Photo by Unseen Studio on Unsplash
Photo by Unseen Studio on UnsplashThere are many advantages to learning Morse code:
Emergency preparedness: Morse code can be a crucial tool for survival when emergencies happen, especially in remote places where technological failure is common.
Boosting cognitive abilities: Mastering Morse code improves mental skills like focus, quick decision-making, and interpreting the message of sounds and visuals.
A popular hobby: Amateur radio fans use Morse code (also known as CW or Continuous Wave) as an enjoyable way to communicate.
Fun and rewarding: Learning Morse code is both fun and challenging, offering a great sense of accomplishment as you advance from recognizing individual letters to decoding full messages.
Take Action

Start learning more about Morse code, keep developing your listening and transcribing skills, and connect with other Morse coders with these resources:
Your feedback matters to us.
This Byte helped me better understand the topic.
