You're going about your day as usual when all of a sudden your cell phone shuts off unexpectedly...AGAIN! It's the 3rd time it's happened this month. 😣

What should you do? Just restart it and hope for the best? Or try to get to the bottom of the problem?
If you want to find out the real problem and really fix it, you'll need to conduct a root cause analysis.
What is a Root Cause Analysis?
It's when you analyze a problem to find the underlying cause.
Knowing what caused a problem helps you prevent it from happening again.
Many large industries and organizations use root cause analyses as part of their business practices. Using it effectively can prevent harm and even save lives!

For example, when a surgery goes wrong at a hospital, doctors and staff gather afterwards to analyze what happened and make changes so that future surgeries go better.
Root cause analysis can also be helpful for you at work and in your daily life.
Quick Quiz!

Mara gets a headache around 3 PM several days a week. When she takes an aspirin, it goes away. She decides to take an aspirin at 2 PM every day to fend off the upcoming headache.
Quiz
Did Mara conduct a root cause analysis in regards to her headaches?
The End Goal
The ultimate purpose of a root cause analysis is to find lasting solutions.

Once you've determined the cause, you'll ask, "How can I make sure it doesn't happen again?" Then it's important to implement solutions that address the root cause.
Example
Problem: The fire alarm outside the college biology lab has gone off 3 times this month. Each time, the building had to be evacuated and the fire department responded in full force. However, there was never a fire. It's becoming problematic for all involved.
Root Cause: After conducting a root cause analysis, the fire department and biology staff determined that the combination of an old smoke detector and chemical residue in the air from formaldehyde were resulting in faulty signals in the alarm apparatus.
Solution: The smoke detector was updated and an air filter was installed in the lab. Other smoke detectors in the building were also updated so that they wouldn't malfunction.
Method 1: The 5 Whys

One way to conduct a root cause analysis is to ask WHY 5 times:
Example
You tripped on the stairs at home this morning.

Why? It was dark and you took a misstep.
Why? The hall light wasn't working.
Why? The bulb went out and no one changed it.
Why? We didn't have extra bulbs.
Why? No one put it on the shopping list.

Solution: Keep a supply of bulbs on hand and set a reminder to replenish the supply when only a few are left.
Method 2: Change Analysis

For this method, you'll identify what changes happened leading up to the event that differ from the regular routine. Change analysis is best to use if the problem is complex or if there could be multiple causes. You may have to go back quite a bit in the timeline to find out what changed.
Questions to ask if using this method include why, how, and especially: what changed?
Example
Flyaway Airlines cancelled hundreds of flights over the busy holiday season, leaving travelers stranded and disgruntled.
 Process:
Process:
Top managers consulted with representatives from all airline departments to try to find the root of the problem.
By asking the questions "Why? How? and What changed?" they pinpointed the underlying cause: the flight crew scheduling system had been malfunctioning for the past year. When extra flights were scheduled for the holidays, it totally crashed.
Solution: Flyaway Airlines immediately upgraded the flight crew scheduling software.
Quiz
What questions could Flyaway Airlines ask during the Change Analysis process?
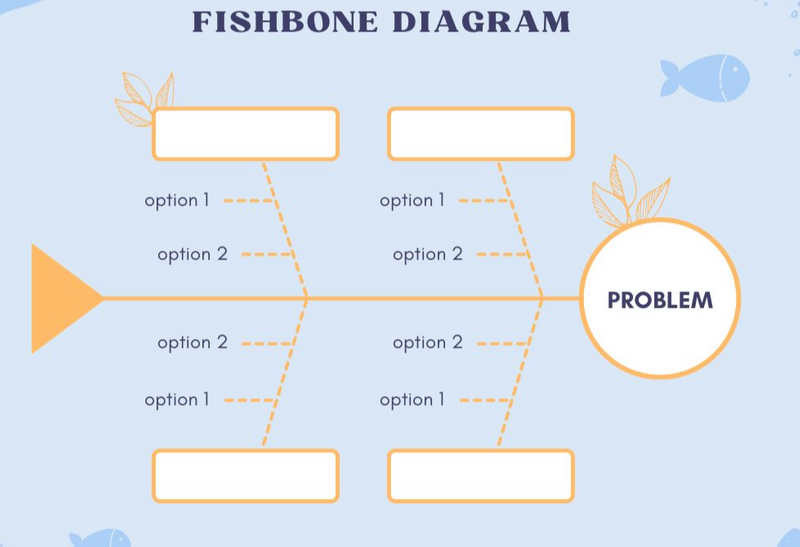
Method 3: Fishbone Diagram

This method is best used to brainstorm what the cause(s) of the problem could be.
Gather the team and proceed as follows:
Draw a fish-shaped diagram
Write the problem in the "head" box
Write main categories that may have contributed to the problem in the boxes at the end of the "ribs"
Write more specific points for each category as people discuss the potential causes
Example
Nature's Farm delivers milk to 100 local grocery stores. Recently, a number of shipments were returned due to the milk being spoiled.
Process:
Managers gather and write down the problem. Now they brainstorm primary areas that could have caused the milk to spoil. These include:
Machinery
Training of personnel
Shipping procedures
Cow care
Next they add ideas of problems relating to each category. The resulting diagram might look something like this:
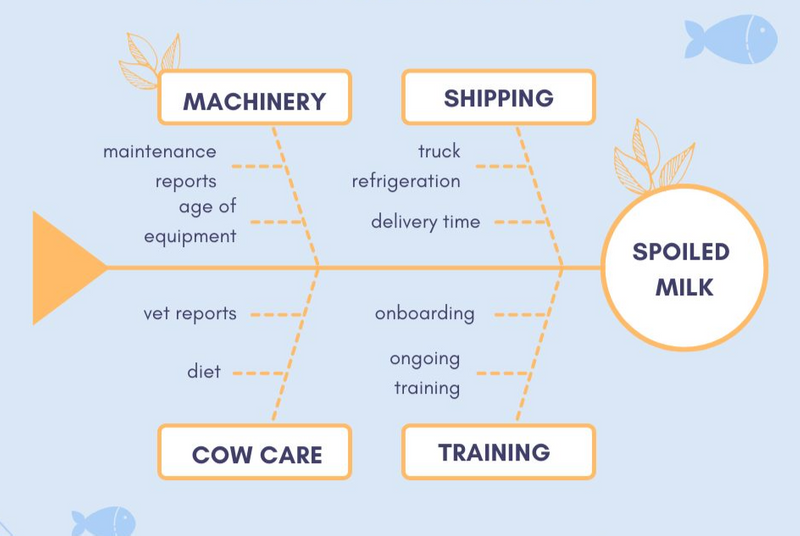
Solution: After exploring each of the possible causes, Nature's Farm determines thatthe spoiled milk was the result of new workers who weren't adequately trained to operate the machinery. They updated their new hire training process.
Mara's Headache
Remember Mara, who has been getting 3 PM headaches on some days? She knows it's probably not healthy to take an aspirin every day, and decides to find out what is causing her headaches by conducting a root cause analysis.
Quiz
Which root cause analysis method would be best for Mara to use? Select all that apply.
Take Action

The next time you experience a problem:
Your feedback matters to us.
This Byte helped me better understand the topic.

